What is Phos-tag™?
Phos-tag™ is a functional molecule developed at the Hiroshima University's Functional Molecular Science Laboratory, which traps the phosphate monoester anions (R-OPO32) at neutral pH (physiological pH). Phos-tag™ is a breakthrough method for the separation, purification, and detection of phosphates (R = protein, peptides, etc.).
Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of proteins are crucial elements of biological functions and considered to be important in signal transduction. The elucidation of the phosphorylation process is a main topic in post-genome research and has become a target of drug discovery.
Conventional techniques and their issues
Enzyme Immunoassay
- Uses an antibody's ability to bind to targets (antigen).
- Target-specific antibodies must be produced, and targets (antigen) must be isolated and purified.
- Because the immune response in animals is used in producing antibodies, time is required for antibody production.
- Antibodies cannot be produced at the phosphorylation sites of a molecule smaller than a few kDa.
Method of using radioactive isotopes
- Radioactive isotope 32p is used.
- Management of radiation and waste solution requires considerable care.
Phos-tag™ benefits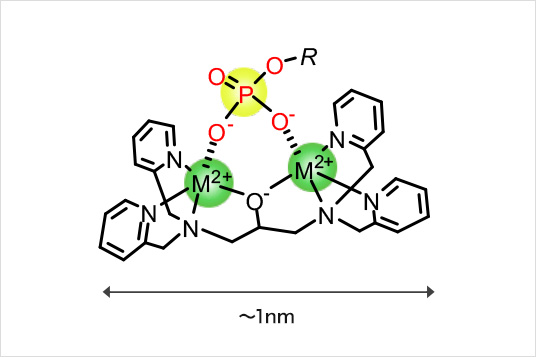
Phos-tag™ binds to anionic substituted groups, particularly to divalent phosphomonoester anions, under neutral (physiological) conditions. Unlike conventional enzyme immunoassays and radioisotopic methods, Phos-tag™ enables the trapping of substances with anionic substituted groups, particularly divalent phosphomonoester anions, and stabilizes certain types of phosphate compounds that are not easily measured due to their instability. The trapped compounds usually release anionic compounds at pH values of 3 to 4
Applications
In biochemistry, Phos-tag™ can label almost all the compounds, such as proteins and nucleic acids, with a phosphate group. Utilizing this property, the following applications are considered to be possible. By capping the phosphate group of the phosphate compounds, unknown donors can be detected based on the spinning and mass differences from the control sample generated by nuclear magnetic resonance and mass analysis. The addition of Phos-tag™'s electric charge causes electric and mass changes, which can be used for electrophoresis and chromatography. When Phos-tag™ is bound to plates, resin beads, or fibers, donors are captured, and the phosphorylated compounds can be separated from the non-phosphorylated compounds. Furthermore, by selectively binding Phos-tag™ to plates, resins beads, or fibers, we can separate compounds according to the number of phosphate groups.
Phos-tag™ Product Listing
Separation of phosphorylated peptides
Electrophoresis reagents
|
Phos-tag™ Acrylamide |
Internal capacity |
Loading amount (product) |
|
AAL-107 |
10mg |
Phos-tag™/Acrylamide=1/1 |
|
AAL-107M |
2mg |
Phos-tag™/Acrylamide=1/1 |
|
5 mM aqueous solution AAL-107S1 |
0.3mL |
Phos-tag™/Acrylamide=1/1 |
|
Phos-tag™ |
Internal capacity |
Loading amount (product) |
|
5 × |
Phos-tag™ 50µmol/L 6-15% |
Collection of phosphorylated peptides
Affinity chromatography products
|
Phos-tag™ Agarose |
Internal capacity |
Loading amount (product) |
|
AG-501 |
0.5mL |
3~5 µmol Phos-tag™/mL-gel |
|
AG-503 |
3mL |
3~5 µmol Phos-tag™/mL-gel |
|
Phos-tag™ Tip |
Internal capacity |
Loading amount (product) |
|
AG2-103 |
8 × |
3~5 µmol Phos-tag™/mL-gel |
Observation of phosphorylated peptides
Detection on PVDF membrane and increased sensitivity of quantitative analysis
|
Phos-tag™ Biotin |
Internal capacity |
Loading amount (product) |
|
BTL-111S11mM aqueous solution |
0.1mL |
Phos-tag™/Biotin=1/1 |
|
BTL-104 |
10mg |
Phos-tag™/Biotin=1/1 |
|
Phos-tag™ |
Internal capacity |
Loading amount (product) |
|
MS-101KIT |
1set |
MS-101L 5mg |
